FROM EDITOR-IN-CHIEF
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Actuality. This article presents the results of clinical studies of trimebutine maleate in functional gastrointestinal disorders (GIT).
The objective of the work is to analyze the use of trimebutine in clinical practice from the standpoint of efficacy and safety according to the results of clinical studies published in the literature.
Since the late 1960s, trimebutine maleate has found wide application in the treatment of functional GIT disorders, including functional dyspepsia (FD), functional biliary tract disorders (FDBT), and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Trimebutine is usually classified as an antispasmodic, but its unique properties make it a multifunctional drug. The efficacy of trimebutine for treating IBS has bee n confirmed in several meta-analyses and reviews. One of the first clinical studies showed that the drug effectively affected stress-induced motility disorders and abdominal pain in patients with IBS. A meta-analysis including 26 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) demonstrated the high efficacy and safety of trimebutine compared with other antispasmodics and placebo. Its efficacy was also confirmed for treating functional abdominal pain and dyspepsia in a meta-analysis of 22 RCTs involving 1,778 patients with IBS. In 2011, trimebutine was included in the Cochrane systematic review of drugs with different mechanisms of action for treating IBS. Numerous studies have demonstrated the effect of trimebutine on upper gastrointestinal motility and its efficacy as an antispasmodic and prokinetic agent for treating FD. The safety of trimebutine was also noted in postoperative paralytic ileus. Adverse reactions such as dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and dry mouth were reported in 4.1 % of cases (14 of 340 patients). It should also be noted that trimebutine is safe to use in pediatric practice. According to clinical studies, mild to moderate adverse reactions were observed in 7 % of patients treated with trimebutine, while no adverse effects were reported in more than 1.8 % of patients, and some of them could be related to the patient's health condition rather than the drug.
DRUGS UTILIZATION RESEARCH
This article analyzes the use of the generic drugs trastuzumab for treating breast cancer and their importance in modern medicine and biotechnology. Statistics on breast cancer in the Russian Federation show a steady increase in the detection of this type of cancer from 2011 to the present. As a result, the need for new and more effective treatment methods is increasing. In modern medicine, generic drugs are increasingly used, the cost of which is significantly lower than the original drug, and their use does not have a negative effect on the effectiveness of treatment. A comparative analysis of existing treatment methods, such as chemotherapy, surgery, and targeted therapy using monoclonal antibodies, was carried out. A deficit of trastuzumab-based drugs on the Russian market was identified based on an extensive analysis of statistical data, drug prices and purchase volumes, which allowed us to conclude that it is advisable to use generics of trastuzumab in the treatment of breast cancer to reduce the economic burden on healthcare and increase the availability of treatment. The results of the analyze can be used as a justification for the need to increase the production of domestic generics for the treatment of breast cancer.
NEUROLOGY
The glymphatic system in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) is an important object of research because it plays a key role in the removal of metabolites and maintenance of homeostasis in the central nervous system. In MS, which is characterized by demyelination and inflammation, the functions of the glymphatic system may be impaired, leading to the accumulation of toxic substances in the brain and aggravation of neurodegenerative processes. Understanding the relationship between the
glymphatic system and MS will provide new horizons for potential therapies and may help improve the clinical condition of patients and slow disease progression.
INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Actuality. In recent years, there has been a growing relationship between HCV infection and metabolic syndrome. Studies have shown that metabolic disorders can worsen the course of chronic hepatitis C, increasing the risk of disease progression and liver fibrosis.
Objective. To identify the clinical, laboratory, and genetic characteristics of patients with HCV and metabolic disorders.
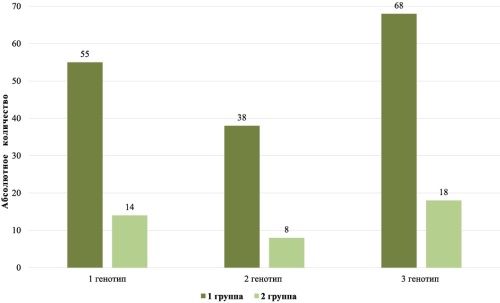
Materials and methods. 201 patients aged 18–60 years were examined at the Yaroslavl Regional Infectious Diseases Clinical Hospital. Anamnestic data were collected, and anthropometric measurements were performed. The diagnosis of hepatitis C was verified based on the detection of a spectrum of antibodies (a-cor, a-NS3, a-NS4, a-NS-5) in blood serum by enzyme immunoassay (ELISA), as well as HCV RNA using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The molecular genetic study was conducted on the basis of the clinical and diagnostic laboratory of the Institute of Pharmacy of Yaroslavl State Medical University. The gene polymorphism was tested using real-time PCR on an iCycler iQ5 (BioRad) device with a set of SNP-express-RV reagents. Polymorphisms of the following genes were studied: APOE Leu28Pro, LPL S447X, and FTO A23525T.
Results. According to the inclusion criteria, the patients were divided into two groups: the first (main) group was HCV with metabolic syndrome (161 people), and the second (comparison group) group was chronic hepatitis C without MS (40 people). Direct correlations have been established between the presence of mutations in the LPL S447X and FTO A23525T genes
in patients with a high degree of hepatitis activity, stages of AF F3-F4, dyslipidemia, and the severity of the components of metabolic syndrome.
Conclusion. Metabolic disorders significantly aggravate the course of HCV infection and are more often associated with liver fibrosis progression.
TRAUMATOLOGY AND ORTHOPEDICS
Objective. To study the effect of the PPARG gene on the course of purulent complications after lower limb bone injury treatment.
Materials and methods. A prospective genetic study was conducted involving 114 patients who were treated at the N.V. Solovyov Hospital (Yaroslavl) in the period from 2018 to 2024 for purulent-inflammatory complications after lower limb injuries from 2018 to 2024.
The polymorphism of the PPARG C1431T gene (rs3856806), which plays a key role in the regulation of the inflammatory response and reparative processes, was used as the object of research.
Genotyping was performed using real-time PCR followed by restriction analysis. Statistical data processing was performed using the χ2 criterion to assess the correspondence between genotype distribution and the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium.
Results. Analysis of the allelic distribution of the PPARG gene revealed the prevalence of the C allele in the total sample (82% in the main group and 89% in the control group). The most common genotype was C/C (70% and 80%, respectively), which indicates its association with a lower predisposition to infectious complications. The distribution of genotypes was in accordance with the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (p > 0.05), confirming the representativeness of the sample.
Conclusion. The PPARG C1431T polymorphism is a significant predictor of the risk of developing and relapsing purulent complications in patients with lower limb injuries. Carriers of the T allele exhibit an increased likelihood of a prolonged inflammatory response, which requires a personalized approach to antibiotic therapy and early immunocorrection. To improve the accuracy of the forecast, it is necessary to take into account covariates, namely: metabolic disorders (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2, type 2 diabetes mellitus), cardiovascular pathologies (hypertension, coronary heart disease).
UROLOGY AND ANDROLOGY
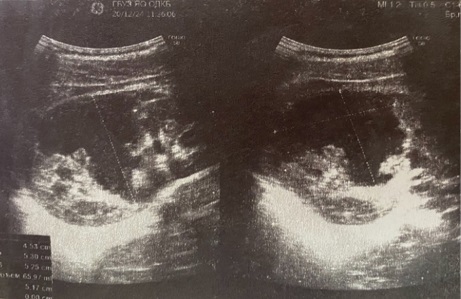
Introduction. Injury to the epididymis is a rare type of injury, accounting for no more than 2–5 % of cases of injury to the scrotum. Preoperative diagnosis is difficult and effective in no more than 70 % of cases. Long-term results have no less negative consequences than damage to the testicular parenchyma proper due to the development of obstructive azoospermia. The low coverage of the issue in the literature and the sparseness of observations make it possible to consider the addition of information on this section of urgent andrology appropriate.
Materials and methods. Seven cases of testicular appendage damage are presented, of which 5 are isolated and two are combined with testicular damage. The average age of the patients was 13 years and 5 months (9–17 years).
Results and discussion. Several cases of appendage damage, both isolated and combined with testicular damage, are described. The possibilities of ultrasound diagnostics have been analyzed, for which the effectiveness is 71.4 %, which is significantly lower than for testicular damage. An active surgical tactic is demonstrated as the most optimal in case of violation of the capsule integrity. The presented injuries are considered as disrupting the function of the appendage with the development of obstructive azoospermia on the side of the injury.
Conclusion. Testicular appendage injury is a poorly studied type of injury that requires further refinement of diagnostic criteria, development of therapeutic tactics and evaluation of treatment results. Active surgical tactics are the most optimal method of patient management. In all cases, the outcome of appendage injury with a violation of the integrity of its capsule should imply a high risk of obstructive azoospermia.
ANESTHESIOLOGY AND RESUSCITATION
The incidence of cardiac complications after non-cardiac surgeries remains extremely high. There are clinical guidelines that describe potential predictors of such complications. Three clinical cases of cardiac complications in patients after elective vascular surgeries are presented that could have been avoided using prognostic tests and pharmacological cardioprotective measures.
PHYSICAL AND REHABILITATION MEDICINE
The article presents the results of using a water bike simulator during medical rehabilitation of young and middle-aged patients with the consequences of lower limb trauma.
Objective. Evaluation of the dynamics of cardiovascular system parameters and bioimpedance analysis parameters when using a water bike.
Materials and methods. The study involved 87 people who were divided into two groups: study and control. The course duration was 14 weeks. During the examination, the following parameters were assessed: hemodynamic parameters, body composition (bioimpedance analysis), anthropometric parameters.
Conclusions. The use of a water bike simulator in rehabilitation can improve functional fitness and general health of people, thereby reducing the period of rehabilitation treatment after injury or surgery, ensuring high efficiency of the patient's return to a full life.
Relevance. In the context of the growth of chronic diseases and psychoemotional stress, the search for accessible, motivating and multifactorial methods of health improvement is of particular importance. Ballroom dancing combines physical activity, creative realization and social involvement, which makes them a promising direction for prevention and rehabilitation.
Objective. To study the effect of regular ballroom dancing on the physical, psychoemotional and social health of adults.
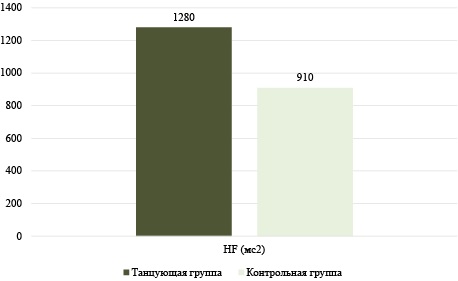
Materials and methods. The prospective controlled study involved 68 people (34 — the main group, 34 — the control group), aged from 22 to 64 years. The following methods were used: questionnaires, SAN questionnaire, Spielberg anxiety scale, heart rate variability measurements (HF component), as well as the author's motivation scale (1–7 points). Statistical processing was carried out in the Stattech package, with a significance level of p < 0.05.
Results. Participants in the main group demonstrated a significant improvement in motor coordination, a decrease in anxiety (by 10.7 points on the Spielberg anxiety scale, p < 0.001), an increase in the HF index (by 24.8 %, p < 0.01), improved sleep, increased self-esteem and expanded social activity. The level of motivation for physical activity in the main group was 6.2 points versus 3.7 in the control group (p < 0.001). Correlation analysis revealed significant relationships between the duration of classes, health level and emotional stability.
Conclusions. Dance therapy in the form of sports and ballroom dancing has a systemic positive effect on the body. A high level of motivation makes dancing a promising tool for sustainable health improvement. This method deserves widespread implementation in the practice of preventive and restorative medicine.
MEDICAL CYBERNETICS
The paper analyzes the role and prospects of large language models (LLMs) in the transformation of modern healthcare, with a focus on improving doctor-patient interactions. The spectrum of LLM applications is considered: from automating administrative tasks to supporting patients in self-education and managing their health. It reveals the ability to semantic adaptation, to translate complex medical terminology into a language understandable to the patient, which supports the concept of shared decision-making. Practical cases of LLM application are highlighted, including monitoring chronic disease, supporting adherence to drug therapy, and providing instructions in emergency situations. Accepting the problems of accuracy of publicly available LLMs, the possibility of generating false information (“hallucinations”), data bias, and ethical and regulatory challenges related to data privacy and accountability for the information provided, technological aspects such as Retrieval-Augmented Generation search architectures and Chain of Thought techniques to improve the accuracy and clinical relevance of LLM-generated responses, and voice interfaces as a means of improving the accessibility of these technologies to diverse populations are disclosed. The need for interdisciplinary collaboration and a clear regulatory framework for safe and effective implementation of technologies in clinical practice is emphasized.
EDUCATION
The paper The introduction of a competency-based approach into higher education involves the transformation of not only the content of curricula, but also the updating of pedagogical strategies. The emphasis on active and interactive formats of interaction instead of traditional passive methods creates conditions for the targeted development of students' professional skills. This approach helps to develop the ability of future specialists to build a productive dialogue in work situations, apply digital technologies for data analysis and self-development, and find non-standard solutions to practical problems. These aspects directly affect the level of professionalism of graduates, enhancing their competitiveness and adaptability in a dynamically changing environment. The integration of modern educational tools into the learning process is becoming a key factor in ensuring a harmonious combination of theoretical training and practice-oriented thinking.
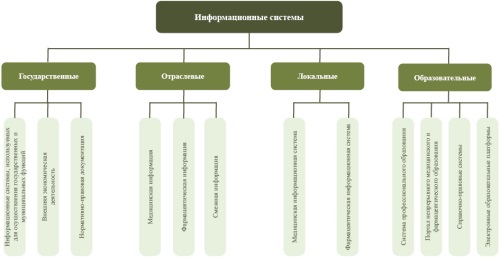
Relevance. The knowledge of future medical and pharmaceutical workers about healthcare information systems is an integral part of drug provision in the provision of medical care. The willingness of students to use information technology contributes to the formation of qualified and sought-after specialists in the modern labor market.
Methodology. Methods of content analysis, the method of expert assessments, questionnaires, grouping, comparative and structural analysis, mathematical and statistical methods were used. The analysis of the regulatory framework in the field of healthcare information support has been carried out. The requirements of professional standards for healthcare professionals on the use of information technology in their professional activities have been studied. A survey of medical university students
in the fields of medicine, pediatrics, dentistry and pharmacy was conducted based on the proposed classification of healthcare information systems.
Results. Sufficient awareness of medical university students about information systems and their readiness for use in professional activities has been revealed.
Conclusion. The formation of appropriate information skills of young healthcare professionals in order to provide high-quality medical and medicinal care is ensured through coordinated actions by the state, educational institutions and medical and pharmaceutical organizations-employers.
Адрес редакции и издательства:
ООО «Издательство ОКИ»
115522, Москва, Москворечье ул., 4-5-129
Генеральный директор Афанасьева Елена Владимировна
Тел. + 7 (916) 986-04-65; Email: eva88@list.ru


































.png)
