FROM EDITOR-IN-CHIEF
RADIATION DIAGNOSTICS AND THERAPY
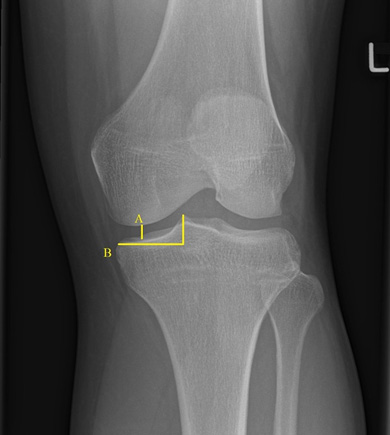
Objective. To study the features of X-ray manifestations of knee joint arthrosis in women of different ages, depending on bone mineral density and severity of X-ray morphometric signs of osteopenia and osteoporosis of the spinal.
Materials and methods. The study involved 82 women aged 50 to 77 years, divided into three unequal age groups (50–59, 60–69, 70 years and older); to assess the X-ray morphometric signs of osteopenia and osteoporosis, standard radiographs of the thoracic and lumbosacral spine in two projections were used; manifestations of gonarthrosis were assessed by the results of radiography of the knee joints in a direct projection — the index of the knee joint was calculated, and a semi-quantitative assessment of characteristic x-ray changes was made; Quantitative X-ray computed tomography on a Somatom CT (Siemens) of 2, 3, and 4 lumbar vertebrae was used as an absorptiometry technique.
Results. As expected, a decrease in the index of the knee joint index with increasing age was observed. In the oldest age group (over 70 years), with minimal bone mineral density and the most pronounced X-ray manifestations of osteopenia and osteoporosis of the spinal column, there was no significant increase in the prevalence of manifestations of arthrosis of the knee joints in the form of subchondral osteosclerosis and bone growths along the edges of the articular surfaces.
Conclusions. The results of this study establish the relationship between bone mineral density and X-ray manifestations of arthrosis of the knee joints in the form of subchondral osteosclerosis and marginal bone growth.
RHEUMATOLOGY
Relevance. Activation of innate and acquired immunity, accompanied by increased production of classical (interleukin (IL) IL-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interferon-γ (INF-γ)) proinflammatory cytokines in synovial fluid and blood serum, plays an important role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Objective. To determine the concentration of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and INF-γ in RA patients in the advanced stage of the disease, to evaluate the relationship between them, clinical indices of disease activity, the presence of rheumatoid factor (RF), and antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide (ACCP).
Material and methods. We examined 154 patients with RA (41 men and 113) who were middle-aged (56.0 (50.0; 64.0) years), disease duration (9.4 (3.0; 13.0) years), seropositive 129 (83.8 %) for IgM RF and/or 106 (68.8 %) ACCP with moderate to high (DAS28-ESR — 5.40 (4.65; 6.00)) disease activity. The concentration of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and INF-γ in serum determined by multiplex technology.
Results. The concentration of IL-1β was not significantly different between patients with RA and controls. The values of IL-6 and INF-γ were significantly higher, and TNF-α — significantly lower than in donors. IL-6 hyperproduction was detected most frequently (51.6 %), whereas elevated levels of INF-γ (38.96 %), IL-1β (26.62 %) and TNF-α (23.38 %) were less common. Significant positive correlations were observed between the concentrations of all cytokines and their high levels. The strongest correlations were characteristic for IL-1β, TNF-α and INF-γ. No statistically significant differences in cytokine levels were observed between patients with RA who were positive or negative for IgM-RF and ACCP. The concentration of IL-6 alone significantly positively correlated with the values of the indices (DAS28-ESR, CDAI, SDAI) of RA clinical activity (p<0.05).
Conclusions. There are differences in the levels and frequencies of proinflammatory cytokines among patients with advanced-stage RA. In the presence of a close relationship between them, there are certain differences in their associations with clinical and laboratory indicators of disease activity.
PHYSICAL AND REHABILITATION MEDICINE
Osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee joints (KJ) has a high social significance and is therefore a relevant pathology for scientific research. The authors have proposed an original hydraulic theory for the pathogenesis of OA in KJ. This approach is based on the notion of primary mechanical damage to the internal ligamentous structures and synovial membrane accompanied by posttraumatic edema, synovial hypervolemia, and hypertension. The authors demonstrated that regular physical activity at all stages of the disease is pathogenetically justified and allows the patient to improve lymphatic and venous outflow and thus resist increasing fibrosis. Improved arterial blood flow will reduce tissue hypoxia. Any type of symptom-modifying therapy can be harmful because it reduces the protective role of pain reflexes in protecting the KJ from excessive loads, leading to injury. The necessity of maintaining a walking speed of more than 4.3 km/h with an increase in cadence is emphasized from the perspective of reducing static stress during walking and extending life expectancy.
Rehabilitation is widely recommended in national and international guidelines for the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA) and is considered one of the main treatment strategies for patients with OA. Osteoarthritis rehabilitation includes physical exercise, strength training, weight-control, and self-control training and includes transitioning to an active lifestyle.
A review of the effectiveness and safety of rehabilitation for the treatment of OA was conducted, and international evidence-based recommendations were analyzed. Physical therapy is widely recommended for the treatment of OA. In this review we focused on exercises on land and water, and strength training for OA. In general, evidence indicates that physical therapy and special strengthening exercises or strength training for the lower extremities can reduce pain and improve physical function in knee joint OA. Data from other OA localities are less reliable. Therefore, considering the lack of special studies, recommendations for treating hip and hand OA are based on studies on knee OA. In addition, no recommendations regarding the exercise regime have been developed. The effectiveness and safety of physical therapy and strength training should be further evaluated in randomized controlled trials involving patients with OA of the hip joint and hands. It is also necessary to define the optimal composition of exercise programs more clearly.
A search of relevant literature was conducted in PubMed and the Cochrane Database from 2014 to March 1, 2024. Exclusion criteria: absence of comparison groups; total number of study participants <20 and premature termination of the study.
NEUROLOGY
Lyme borreliosis is a natural focal, vector-borne disease caused by Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato. The transmission of ixodes ticks is characterized by a staged course with damage to various organs and systems. This disease is an urgent problem in medicine because of the peculiarities of its clinical course, including in the late period. Not infrequently, due to the lack of vigilance of physicians and the polymorphism of the clinical presentation of the disease, Lyme borreliosis runs under the masks of other diagnoses. In Covid-19, caused by the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, both in the acute period of the disease and later develop systemic clinical manifestations in the central and peripheral nervous systems and the musculoskeletal system. These features are particularly characteristic of the post-Covid-19 syndrome.
A clinical case of chronic neuroborreliosis and post-COVID-19 syndrome with lesions in the nervous and muscular systems is presented.
INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Relevance. This article presents the results of clinical studies on the use of antiviral drugs for treating chronic hepatitis C (CHC) and metabolic syndrome (MS).
Objective. Analysis of the effectiveness of CHC therapy and its impact on the components of MS.
Materials and methods. The study was conducted at the Yaroslavl Regional Infectious Diseases Clinical Hospital between 2015 and 2023. All patients were prescribed a standard set of clinical, laboratory, and instrumental examinations upon admission to the hospital (general and biochemical blood tests, blood tests for HCV genotype and viral load, ultrasound of the abdominal organs). Treatment was performed using different antiviral regimens.
Results. Among the regimens used, only interferon-containing regimens resulted in changes in the components of metabolic syndrome. A significant decrease in abdominal obesity and triglyceride levels was observed (p< 0.05) The changes mainly affected patients with genotypes 2 and 3, which confirms the "viral" genesis of the development of these components of MS.
ANESTHESIOLOGY AND RESUSCITATION
Relevance. A critical task of modern anesthesiology and resuscitation is the prediction and diagnosis of cardiac complications after non-cardiac surgeries. There are clinical guidelines for reducing the incidence of such complications; however, in practice, routine implementation of the full-risk stratification algorithm is not always performed. Objective. To assess the possibility of predicting and diagnosing cardiac complications after non-cardiac surgeries in medical organizations of constituent entities of the Russian Federation with a population of less than 1 million people. Materials and methods. An anonymous online survey of anesthesiologists and resuscitators of one of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation was developed using Yandex Forms.
Results. We processed 62 completed questionnaires. Cardiac complications during the postoperative period are registered by 33 (53.2 %) respondents. Cardiac risk indices were used by 10 (16.1 %) physicians and load tests (treadmill, bicycle ergometry) by 9 (14.5 %). Routine ECG monitoring after surgery was performed by 27 (43.5 %) respondents. Cardiac-specific troponin determination is available to 60 (96.8 %) physicians; however, only 6 (9.7 %) respondents measured it routinely before surgery and 4 (6.5 %) respondents measured it after surgery. Natriuretic peptide or its prohormone determination is available to 19 (30.6 %) physicians; however, only 3 (4.8 %) prescribe it before surgery and 0 after surgery. The possibility of performing echocardiography before and after surgery was noted by 54 (87.1 %) respondents. Only 9 (14.5 %) respondents reported that their hospital could perform coronary angiography.
Conclusions. The results of this survey revealed that many cardiac complications could have been missed because of insufficient preoperative prognosis and postoperative diagnostic data.
UROLOGY
Представлен случай травматической ампутации головки пениса проксимальнее венечной борозды у ребёнка 5 лет при выполнении «ритуального обрезания» вне медицинского учреждения. В ранние сроки после травмы выполнена микрохирургическая реимплантация с хорошими ближайшими результатами.
A case of a rare combined defect - penoscortical transposition and scrotal hypospadias is presented. A two-stage correction of hypospadias was performed, and the second stage was combined with penile transposition, resulting in good functional and cosmetic results.
HISTORY
The article describes the development of the Department of Surgical Diseases at the Yaroslavl State Medical University from 1974 to 2024.
Адрес редакции и издательства:
ООО «Издательство ОКИ»
115522, Москва, Москворечье ул., 4-5-129
Генеральный директор Афанасьева Елена Владимировна
Тел. + 7 (916) 986-04-65; Email: eva88@list.ru



































.png)
