ACTUAL REVIEW
The consideration of pathomorphosis makes it possible to assess the role of various factors in the occurrence, pathogenesis, specific manifestations, and content of pathology, to determine the boundaries of chronological dynamics, its modification, and, accordingly, to orient therapeutic and preventive measures. The urgency of this problem is caused by the rapidly increasing changes that are taking place in the life of modern society, with an abundance of information sources, the increasing activity of medical services to protect the health of the population, and the growth and accessibility of therapeutic possibilities of modern medicine.
Precision and personalized medicine tailors’ therapy, disease prevention, and health maintenance to each individual. Precision and personalized medicine aims to optimize care for individual patients using predictive biomarkers to improve outcomes and prevent side effects. Precision and personalized medicine combined with pharmacogenomics.
This article examines the current path of personalized medicine from a broader perspective with the goal of finding a better direction for its future development. Based on the analysis and demonstration of the research methods and problems found in precision medicine research, as well as its scientific limitations, this review points out that although precision medicine belongs to the model of personalized medicine, it cannot yet achieve the ideal personalized medicine on its current path development.
SURGERY
Relevance. Despite many studies devoted to diverticular colon disease, the results of treatment of this pathology cannot be considered satisfactory. This is primarily due to the fact that the pathogenesis of this pathology has not been fully studied, there are conflicting data on the clinical significance of the level of intraluminal pressure in the intestine and the degree of violation of collagen synthesis in patients. To a certain extent, these criteria can be decisive in assessing the prognosis of the course of the disease in order to timely conduct proactive conservative therapy and adequate surgical aid. The purpose of the study. Improving the results of treatment of patients with complicated course of diverticular colon disease. Materials and methods. There were 194 patients with diverticular colon disease under observation. In 86% of cases, diverticula were localized in the left half of the colon, and isolated sigmoid colon diverticulosis was detected in 68.0% of patients, in the right half — in 4.7% of cases, total diverticulosis — in 9.3% of patients. In patients, the leukocyte intoxication index, the body resistance index, the neutrophil reactive response, the determination of connective tissue dysplasia, connective tissue metabolism indicators, and the measurement of intraluminal pressure in the sigmoid colon were calculated. Results. Conservative therapy was effective in 158 patients (81.4%). Surgical treatment was required for 36 patients (18.6%), with perforation of the diverticulum — in 13.4%, with stenosis — in 5.2% of cases. The nature of the operation was determined by the localization of diverticula and the variant of complication. Postoperative mortality was 2.8%. It was found that connective tissue dysplasia is observed in all patients with diverticular disease, mild — in 36.6% of patients, moderate — in 63.4%. When assessing the intraluminal pressure in 46 patients, its increase was found in all variants of the course of diverticular disease. The average intraluminal pressure was 13.5 ± 0.4 mm Hg. The maximum pressure level was detected in patients with uncomplicated course of the disease. With the development of complications, a decrease in intraluminal pressure was noted. A decrease in intraluminal pressure to 12 mm Hg or less was an unfavourable factor and a predisposition to the development of a complicated course of the disease. The following signs had a significant effect on the recurrence of the disease: age (61-68 years), complications, duration of the disease (more than 4 years), the size of the diverticulum mouth (less than 0.6 cm and more than 1.0 cm), leukocyte intoxication index (more than 2.4 conventional units), the maximum number of rows of the muscle plate of the mucosa and muscle membranes (more than 8.3 and 84 respectively). Conclusions. To predict the course of diverticular disease, a comprehensive analysis of the age of patients, the stage of the disease and its duration, the diameter of the diverticular mouth, the sum of alternative signs of trouble, leukocyte intoxication index, the reactive response of neutrophils, the number of rows of myocytes of the muscle plate of the mucosa and muscle membranes is necessary. Their evidentiary value exceeds 70%. The level of intraluminal pressure in the colon can act as a criterion for the complicated course of diverticular disease.
UROLOGY
Bladder concretions are one of the most frequent and difficult to correct complications of bladder exstrophy. The significant proportion of struvites in the structure of concretions often creates an erroneous opinion about the size of the latter and makes it difficult to choose tactics. A case of staged treatment of bladder exstrophy complicated by the formation of a bladder concretion against the background of the current active inflammatory process is presented. Contact cystolithotripsy is the most preferred and least traumatic method of getting rid of bladder concretion of any size. In the case of anatomical closure of the urethra, access through the appendicostomy is most rational, allowing the insertion of an instrument of sufficient diameter for effective intervention.
RHEUMATOLOGY
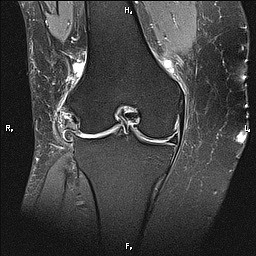
The term "bone marrow edema" (BME) in MRI examination of the knee joint is used to describe areas of decreased signal intensity on T1-weighted images or increased signal intensity on T2-weighted images in the subchondral bone. BME is classified into ischemic (osteonecrosis), mechanical (trauma), and reactive (arthritis) types. In this review, the causes and differences in BME with spontaneous and secondary osteonecrosis and other characteristics of BME transitioning to a syndrome are considered. BME with injuries and bruises is usually reversible and passes after approximately 2–4 months, if accompanied by a cortical fracture, after 6–12 months. A fatigue fracture develops as a result of repeated overloading of normal bone structures, whereas fractures in zones of subchondral bone insufficiency spontaneously occur in pathologically changed bone tissues (for example, osteoporotic bones) without any trauma or overloading. Histological examination of the damaged subchondral bone in ischemic and mechanical BME revealed hemorrhages, microdestruction of bone trabeculae and vascular anomalies, and almost complete absence of direct edema in MRI-positive zones due to increased extracellular fluid content, which can be partially explained by methodological difficulties in detecting increased extracellular fluid by histopathological methods. Prostacyclin and bisphosphonate have been proposed as conservative therapies for ischemic and mechanical BME.
In osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee joints, BME is considered a marker of rapid progression. Data on the influence of obesity, therapeutic exercise and diet, and the use of a cane on BME are presented. Analysis of the effectiveness of conservative therapy revealed a weakly positive response to bisphosphonates. Inhibitors of nerve growth factor (NGF) — monoclonal antibodies to nerve growth factor (like tanezumab and fulranumab) — reduced the severity of pain but led to an increase in the frequency of osteonecrosis and endoprosthesis. Two studies have shown a decrease in the intensity of BME with oral chondroitin sulfate. The attention of orthopedists is focused on subchondroplasty using calcium phosphates. Subchondral filling, which strengthens the bone and replaces the lost barrier function of cartilage, has a symptomatic effect and effectively counteracts the development of BME, although the long-term results need to be studied.
PHYSICAL AND REHABILITATION MEDICINE
This study evaluated the constitutional features, functional state, and physical fitness of young men in strength fitness classes. A comparative analysis of the data obtained at various stages of the annual educational and training cycle was conducted. Significant differences were observed in some anthropometric measurements and an increase in the strength abilities of the subjects at the final stage of the examination.
BIOMEDICAL ETHICS
The article formulates a new legal principle, a new subject of clinical research, suggests considering possible new directions for the development and improvement of ethics and law in clinical research, the role and importance of international organizations in clinical research, identifies practical recommendations for their implementation, identifies new possible subjects clinical research, possible sources for creating an ethical code have been identified.
PRACTICAL RECOMMENDATIONS
The STOPP/START criteria are a comprehensive set of criteria, grouped by physiological systems that define clinically significant problems associated with potentially inappropriate medications (STOPP criteria) and potential prescribing omissions (START criteria). The first two versions of the STOPP/START criteria were published in 2008 and 2015, respectively. Version 3 was updated and validated by a European panel of experts in geriatric pharmacotherapy in 2023 and included 190 criteria aimed at optimizing pharmacotherapy and reducing the incidence of adverse drug reactions in the elderly, especially in the context of multimorbidity and polypharmacy. This article presents the third version of the STOPP/START criteria in Russian Federation.
HISTORY
The article is devoted to the 100th anniversary of the birth of Academician V.A. Nasonova and her huge contribution to the formation and development of the Yaroslavl rheumatology school. The main clinical aspects of the scientific research of Yaroslavl rheumatologists were discussed, which laid a solid foundation for scientific research in this field of medicine, and over the almost 80-year history of the medical university provided training of highly qualified specialists.
BOOK REVIEW
In November 2023, the monograph “Practical issues of rational antibacterial therapy” under. general ed. Yarovoy SK, Khokhlov AL was published. This monograph is devoted to practical issues of empirical therapy for the most common nonspecific infectious and inflammatory diseases. Chapter 1 presents the main provisions of antimicrobial therapy from the perspective of clinical pharmacology. The general patterns of prescription and distribution of antibacterial agents, the concepts of basic and reserve drugs, selection of hospital strains, natural and acquired resistance are explained. Chapter 2 is devoted to a comparison of antibacterial drugs in pairs with each other based on an analysis of their spectra of antimicrobial activity presented in the instructions for use, as well as well-known information about their toxicity and the comparative frequency of dysbiosis. Pairs of drugs for comparison were selected based on actual clinical practice. Chapter 3 discusses combination (multicomponent) antibacterial therapy. Appropriate and possible combinations of two antimicrobial agents have been identified. Recommendations for three-component antibacterial therapy are presented separately. Chapter 4 is entirely devoted to undesirable antimicrobial regimens. Options with insufficient effectiveness, an unsatisfactory safety profile, and those that do not meet epidemiological requirements were analyzed. Chapter 5 is a detailed answer to a purely applied question about replacing a promicrobial agent in three formalized situations: “ineffective”, “unsafe”, “absent”.
The book is intended for clinical pharmacologists, therapists, surgeons and other specialists, students of advanced training courses, and senior students of medical universities.
Адрес редакции и издательства:
ООО «Издательство ОКИ»
115522, Москва, Москворечье ул., 4-5-129
Генеральный директор Афанасьева Елена Владимировна
Тел. + 7 (916) 986-04-65; Email: eva88@list.ru



































.png)
