CLINICAL TRIALS
The results of clinical studies on the use of pirfenidone in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) are presented. The purpose of this study was to analyze the effectiveness and safety of pirfenidone in IPF according to clinical studies published in the scientific literature. IPF occupies an important place in the structure of interstitial lung diseases. Currently, IPF is understood as a condition in which there is chronic progressive fibrotic interstitial aseptic pneumonia of unknown etiology, quickly leading to disability and death. The antifibrotic drug pirfenidone has been approved by the EMA and FDA for use in patients with IPF. The clinical efficacy and safety of pirfenidone have been demonstrated in randomized clinical trials. When using pirfenidone, there were 47.9 % fewer patients with an absolute decrease in FVC ≥10 % or who died, and 132.5 % more patients with no decrease in FVC (p <0.001). In addition, the pirfenidone group had significantly better 6-minute walk test scores (p=0.04) and significantly improved progression-free survival (p<0.001). Long-term use of pirfenidone (up to 72 weeks) significantly reduced the rate of decline in FVC, prevented a reduction in distance traveled in the 6-minute walk test, and increased the time until signs of disease progression appeared compared with placebo. Pirfenidone demonstrated a good safety profile; in most cases, adverse effects were mild, disappeared when the drug dose was reduced, and had no adverse long-term consequences. As a result of a generalized analysis of adverse events recorded in the CAPACITY, ASCEND, and RECAP studies, it was found that long-term (maximum duration was 9.9 years) treatment with pirfenidone was accompanied by nausea in 37.6 % of cases, diarrhea in 28.1 %, dyspepsia — in 18.4 %, vomiting — in 15.9 %, and skin rashes — in 25.0 %.
DRUG SAFETY
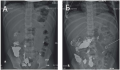
Ceftriaxone-induced urolithiasis is a rare form of urolithiasis in childhood and is accompanied even less often by postrenal (obstructive) acute kidney injury. Its development against the background of acute surgical abdominal disease, for which antibacterial therapy is being performed, seems difficult both from the point of view of diagnosis and treatment. A case of the development of urolithiasis against the background of treatment of appendicular peritonitis complicated by severe acute obstructive kidney injury, which was stopped by minimally invasive methods with subsequent resolution of the obstruction, is presented.
SURGERY
Relevance. The problem of surgical treatment of hernias of the anterior abdominal wall remains relevant. Despite the introduction of new technologies, the results of surgical interventions cannot be considered satisfactory. The development of hernias and their relapses is facilitated by connective tissue dysplasia syndrome, which manifests as phenotypic signs, disorders of the autonomic nervous system, and morphological changes in the structure of the connective tissue.
Objective. To improve the results of surgical treatment of hernias of the anterior abdominal wall in patients with connective tissue dysplasia syndrome.
Materials and methods. The study was based on clinical observations and studies of 497 patients with hernias of the anterior abdominal wall. Inguinal (29 %) and postoperative hernias (21 %) predominated. In the structure of recurrent hernias, postoperative (47 %) and inguinal (42 %) hernias were more often observed. Hernioautoplasty was performed in 31 %, plastic surgery using a mesh endoprosthesis — in 54 %, endoscopic hernioplasty — in 15 % of patients. The severity of the clinical, morphological, and metabolic signs of connective tissue dysplasia syndrome was assessed. The concentration of free hydroxyproline in the blood was determined as a marker of connective tissue metabolism. The state of the autonomic nervous system was assessed using variational pulsometry. To assess the state of collagen in connective tissue, a morphological study of the aponeuroses of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall was performed in the clinic and experiment.
Results. The overall incidence of dysplasia in hernias of the anterior abdominal wall was 48 %. The highest incidence of connective tissue dysplasia was detected in recurrent hernias (70 %). Studies of the level of free hydroxyproline in abdominal hernias have shown the dependence of this marker on the degree of connective tissue dysplasia. In cases of recurrent hernias, the highest intensity of collagen biodegradation was observed. A study of the functional state of the autonomic nervous system revealed a predominance of sympathetic activity in abdominal wall hernias with an increase in the tension index by more than 4 times. An increase in the severity of dysplasia is accompanied by an increase in sympathetic activity. Histological studies in patients with abdominal hernias revealed characteristic changes in the morphological structure of the connective tissue. The average thickness, specific area, brightness of staining, and orientation of collagen fibers in postoperative and recurrent hernias were significantly different compared to the group with primary hernias (p˂0.05). Additionally, an experiment was performed on 30 laboratory animals (white rats) to determine the optimal conditions for healing of the aponeurosis of the anterior abdominal wall. The activating effect of prozerin on the process of histogenesis in the wound was revealed. Based on the results of the study, the surgical treatment of hernias was assessed depending on the type of hernioplasty and the severity of connective tissue dysplasia. It has been established that with increasing severity of dysplasia, the frequency of relapses increases by 2.2–3.4 times. With the progression of dysplasia, the frequency of relapses increased by more than twice. The use of the endoscopic hernioplasty method reduced the risk of recurrent hernias by 9 times.
Conclusion. In externally localized hernias, the incidence of connective tissue dysplasia ranges from 34 % to 70 %. In patients with connective tissue dysplasia syndrome after hernia autoplasty, the frequency of hernia recurrence is 3.4 times higher. Drug correction of sympathetic activity along with alloplasty increased collagen synthesis intensity by 36 %. The choice of hernia repair method should be determined by the type of hernia, the age of the patient, and the severity of connective tissue dysplasia.
UROLOGY
Relevance. Leukoplakia of the bladder is a rare disease, particularly in children. Most studies are based on individual clinical cases, and there are few descriptions of the disease in pediatric practice. Data on the etiology, prevalence, diagnosis, and treatment of the disease are contradictory and are based on adult patients.
Materials and methods. This article describes a clinical case of bladder leukoplakia in childhood.
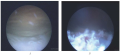
Results. A case of diagnosis and treatment of a 14-year-old patient with leukoplakia of the bladder is presented. The diagnosis of leukoplakia was confirmed by cystoscopy and biopsy of the affected area, after which transurethral resection was performed.
Conclusion. Diagnosis of bladder leukoplakia in childhood is difficult because of the nonspecific nature of the symptoms and the rare occurrence of the disease. The optimal method for the treatment of bladder leukoplakia is transurethral resection of the leukoplakia zone and dynamic follow-up.
PHYSICAL AND REHABILITATION MEDICINE
The relationship between physical endurance performance and microbiota composition is of increasing interest as new evidence points to the importance of intestinal flora as a major determinant of athlete health. The full extent of changes that occur in the microbiota during exercise has not yet been studied. To enhance performance and reduce exercise-induced stress, training programs, combined with individualized diets, aim to balance systemic stressors. Nutrients, especially under conditions of stress, have significant and complete effects on energy metabolism, protein synthesis, and the functioning of the endocrine, nervous, and immune systems. The degree to which nutrients regulate the stress response depends on the duration of the stressor, intensity and type of exertion, the physiologic status of the athlete, and the composition and function of the microbiota. Standard dietary plans are difficult to define because of the individual complexity of the stress response in athletes, ranging from digestive problems to catabolic states and depression. Traditionally, athletes are advised to consume high amounts of simple carbohydrates and proteins and limit fat and fiber intake to provide a quick source of energy and avoid digestive problems associated with high fiber intake. Athletes’ diets are based on the use of foods containing micronutrients such as iron, calcium, amino acids, essential fatty acids, and antioxidants, but the effects of these components on the composition of the intestinal microbiota are poorly understood. Controlled regulation of the microbiota through diet may improve performance during training and competition, reduce stress response, and aid in more efficient recovery of body resources.
MANAGEMENT AND ECONOMICS OF PHARMACY
Relevance. The organization of personalized care with immunological medicines for the prevention of rhesus conflict in Rh-negative pregnant women in outpatient departments of a medical organization using digital labelling is currently relevant.
Methodology. The research used methods of content analysis, grouping, structural and comparative analysis. The analysis of regulatory documentation in the field of treatment of labelled immunological drugs; Clinical recommendations: obstetrics and gynecology; local documents and business processes of the pharmacy of a medical organization, women's consultations, gynecological offices of polyclinics during the prevention of Rh conflict in pregnant women.
Results. Insufficient implementation of digital labelling of immunobiological drugs in outpatient departments of a medical organization has been revealed. The directions of personalized medical care for pregnant women are substantiated: organizational, technical, and educational. Methodological recommendations have been developed for specialists of a medical organization.
Conclusion. The digital labelling of immunobiological drugs will ensure the personalization of drug care for Rh-negative pregnant women in antenatal clinics and polyclinics.
ANESTHESIOLOGY AND RESUSCITATION
Relevance. The quality of postoperative anesthesia may depend on the individual genetic characteristics of the patient. Thus, the C100T and G1846A polymorphisms in the CYP2D6 gene can change the biotransformation of tramadol and, consequently, its clinical effect.
Objective. To evaluate the quality of postoperative pain relief based on tramadol after vascular operations depending on the presence/absence of polymorphisms in CYP2D6, an isoenzyme of cytochrome P450.
Materials and methods. We examined 78 patients aged 52 [49–61] years who underwent routine operations on the vertebral arteries. Every 3 h after surgery, pain was assessed using a visual analog scale. Before and after the operation, variability in heart rate was analyzed according to the method described by Baevsky. The presence of polymorphisms C100T and G1846A in CYP2D6 was determined from whole blood samples. The obtained data were analyzed using nonparametric statistics.
Results. When assessing the CYP2D6 gene, polymorphisms were identified in 22 (28.2 %) patients: G1846A in 18 (23.1 %) patients and C100T in 4 (5.1 %). Patients were retrospectively divided into 2 groups: group 1 (n=56) included patients without studied polymorphisms of the CYP2D6 gene and group 2 (n=22) — with identified polymorphisms. Pain syndrome according to VAS at rest was more intense in group 2 at 18:00, 21:00, and 09:00 on the first postoperative day, when patients were activated — at 18:00 and 09:00 (p<0.05). The stress index after surgery was also higher in group 2 (p<0.05).
Conclusions. The frequency of occurrence of polymorphisms G1846A and C100T of the CYP2D6 gene in vascular patients was 28.2 %. These patients had a more pronounced postoperative pain syndrome and greater activity of the sympathetic nervous system. The determination of these polymorphisms can be used to create an effective personalized plan for postoperative pain relief.
NEUROLOGY
The search for laboratory markers of depression is currently a potential key to understanding the mechanisms of disease development, selecting personalized antidepressant therapy, and defining clear, specific, and objective diagnostic criteria. Identifying biomarkers of depressive disorder offers a broad field for researching many regulatory systems of the body. The laboratory markers identified so far are involved in neurotrophic, neuroendocrine, neurotransmitter, metabolic, and inflammatory processes. This review discusses the use of various biomarkers for studying depression, focusing on the most promising ones.
OBITUARY
Адрес редакции и издательства:
ООО «Издательство ОКИ»
115522, Москва, Москворечье ул., 4-5-129
Генеральный директор Афанасьева Елена Владимировна
Тел. + 7 (916) 986-04-65; Email: eva88@list.ru



































.png)
