Scroll to:
Modern infectious mononucleosis in children: results of own observations
https://doi.org/10.37489/2949-1924-0106
EDN: YTCKUN
Abstract
Background. The relevance of modern infectious mononucleosis (IM) is due to its high prevalence, lifelong persistence of the pathogen in the human body, virus-induced immunosuppression during active viral replication, and the lack of effective treatments and preventive measures.
Objective. To analyze the clinical and epidemiological aspects of infectious mononucleosis in children at the present stage.
Materials and methods. The study included 316 patients hospitalized at the Yaroslavl Regional Infectious Diseases Clinical Hospital between 2021 and 2023.
Results and discussion. The most affected age groups were children aged 4-6 and 11-17 years. The characteristic symptoms of IM remain fever, nasal obstruction, tonsillitis, lymphadenopathy, exanthema, and hepatosplenomegaly. Icteric forms of the disease were rare. In most patients, the onset of rash was associated with the administration of semi-synthetic penicillins at the prehospital stage. Atypical mononuclear cells were detected in only 52.2% of children, making diagnosis based solely on a complete blood count challenging. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) alone or in combination with cytomegalovirus (CMV) was the dominant cause of primary infection. Reactivation was primarily caused by CMV following primary EBV infection in almost all patients. In most children with tonsillar exudate, a low C-reactive protein level indicated a viral etiology of tonsillitis and argued against the need for antibiotic therapy.
For citations:
Kuzmina M.N., Eshmolov S.N., Klimovitskaya E.G., Sitnikov I.G. Modern infectious mononucleosis in children: results of own observations. Patient-Oriented Medicine and Pharmacy. 2025;3(3):77-85. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.37489/2949-1924-0106. EDN: YTCKUN
Introduction
At the present stage, infectious mononucleosis (IM) is one of the most pressing healthcare problems. Its medical and social significance is determined by its widespread occurrence, lifelong persistence of pathogens in the human body, persistent immunological changes during periods of active infection, and the lack of effective treatments and preventive measures [1].
Infectious mononucleosis is a polyetiological disease characterized by a symptom complex including fever, tonsillitis, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and changes in the hemogram (lymphomonocytosis and the presence of atypical mononuclear cells). For a long time, the development of IM was associated exclusively with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection – human herpesvirus 4 [2]. It has now been proven that the etiological factors of this disease also include cytomegalovirus (human herpesvirus 5) and human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6).
All IM pathogens belong to the Herpesviridae family, contain double-stranded DNA, and have a capsid and an outer envelope. EBV belongs to the gammaherpesvirus subfamily with a complex antigenic structure: surface antigens (viral capsid antigen; VCA), early antigens (EA), and nuclear antigens (nucleus antigen-1, -2; NA). Determining specific antibodies to these antigens helps clarify the phase of the infectious process: primary infection, reactivation, chronic infection [3, 4]. A feature of EBV is its tropism for CD21 receptors on B-lymphocytes, as well as for T-lymphocytes and lymphoid tissues. The virus stimulates cellular proliferation and can persist for extremely long periods inside the nucleus of target cells or remain there in a latent state for life [5].
CMV belongs to the betaherpesvirus subfamily. Its double-stranded DNA is the largest among all herpesviruses. Glycoproteins B and H in the outer envelope are the main factors in forming the humoral immune response. Between the envelope and the capsid are tegument proteins (pp71), which can remain in the cell cytoplasm or enter the nucleus. When the protein is in the cytoplasm, the infection remains asymptomatic; upon penetration into the nucleus, active CMV infection develops – either manifest or reactivation of a latent one. CMV has a cytopathic effect, manifested by the formation of giant cells 25-40 µm in diameter with intranuclear inclusions [5, 6].
HHV-6 belongs to the betaherpesvirus subfamily and is divided into two variants (A and B), differing in nucleotide sequences, reactions with monoclonal antibodies, pathogenicity levels, and tissue distribution [5].
The high rate of herpesvirus infection in the population is largely due to the variety of transmission routes: airborne droplets, contact-household, sexual, parenteral, and transplacental [1].
According to the existing classification, IM can occur in typical or atypical forms. During the primary encounter with herpesviruses, the clinical picture of the typical form of the disease develops in only 18% of cases; in others, a primarily latent form or an acute respiratory infection may manifest. In most patients, IM symptoms resolve spontaneously within 1-3 months, but there are exceptions: prolonged course (more than 3 months), chronic course (more than 6 months) [7, 8].
Infectious mononucleosis can be caused by a primary encounter with an etiologically significant pathogen or its reactivation. IM caused by EBV reactivation is detected in 18.2-84.6% of all cases in children across different age groups; for CMV infection – in 39-51%, often with the development of an atypical form with prolonged fever and lymphadenopathy [8]. The laboratory finding of CMV reactivation indicates a combined etiology of the disease [9].
The clinical blood test in IM shows leukocytosis with lymphomonocytosis, and the presence of broad-plasma and basophilic lymphocytes. A characteristic sign is the appearance of atypical mononuclear cells in the first week of the disease, which are detected for 2-3 weeks from the onset but sometimes persist for up to 1 month or more [10]. Currently, the most significant for diagnosis is the detection of virus-specific antibodies in the blood of patients using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). As an additional diagnostic method for IM, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used to detect herpesvirus DNA in the blood and/or saliva of patients. A significant drawback of this method is the high percentage of false-negative results, as DNA is available for verification only during viral replication [4, 9].
Treatment of IM is carried out considering the clinical manifestations, severity, and stages of the disease. Anti-herpetic drugs – acyclic nucleosides – are poorly effective against EBV, CMV, and HHV-6 and therefore are not widely used in the treatment of IM. Antibacterial therapy (cephalosporins, macrolides) is prescribed considering the etiology of tonsillitis and the development of complications (otitis, sinusitis, pneumonia). Due to the high risk of rash in IM, the use of semi-synthetic aminopenicillins is contraindicated [7]. In severe forms of IM with airway edema and obstruction, polyserositis, and severe toxic-allergic rash, glucocorticosteroids are indicated for a course of 3-5 days. Pathogenetic therapy includes detoxification, and according to indications – desensitization and hepatoprotective drugs. Patients with IM are prescribed symptomatic agents (antipyretics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antiseptics for throat irrigation) [11].
Objective
To analyze modern aspects of infectious mononucleosis in children.
Tasks: To study the clinical manifestations, laboratory parameters, and etiological structure of the disease; to analyze a clinical case of the icteric form of IM in a 13-year-old child.
Materials and Methods
The study observed 316 children with infectious mononucleosis hospitalized at the Yaroslavl Regional Clinical Infectious Diseases Hospital in 2021-2023.
All patients underwent analysis of clinical manifestations over time and a complex of laboratory tests, including: complete blood count with determination of atypical mononuclear cells, biochemical blood analysis (bilirubin and its fractions, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase, C-reactive protein (CRP), total protein, creatinine, urea, glucose); prothrombin index (PTI); serological blood testing by ELISA for anti-EBV VCA IgM, anti-EBV EA IgG, anti-EBV NA IgG, anti-CMV IgM and IgG; PCR of blood plasma for EBV DNA, CMV DNA, and HHV-6 DNA; complete urinalysis and urine α-amylase; throat swabs for Corynebacterium diphtheriae and flora with antibiotic sensitivity determination by bacteriological method, for respiratory viruses – by PCR; stool tests for helminth eggs and protozoan cysts, perianal swab for enterobiasis, stool tests for enteric pathogens twice, for rota- and noroviruses by ELISA (as indicated). Instrumental methods included ultrasound examination (US) of the abdominal organs; chest X-ray and X-ray of the paranasal sinuses, electrocardiography (as indicated).
Mathematical processing of the obtained data was performed using MS Excel 2013. Student's t-test was used for statistical analysis. Differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05.
Results
In 2021, 103 (32.6%) patients with infectious mononucleosis were treated; in 2022 – 100 (31.6%); in 2023 – 113 (35.8%). The number of patients by year of observation was approximately the same with a slight increase in 2023.
Distribution of cases by age: children under 1 year – 3 (1.0%); from 1 to 3 years – 74 (23.4%); from 4 to 6 years – 98 (31.0%); from 7 to 10 years – 58 (18.3%); from 11 to 17 years – 83 (26.3%). The largest number of patients was in the 4-6 years group (31.0%; p < 0.05) and the 11-17 years group (26.3%; p < 0.05). The lowest incidence was observed among children under one year (1%).
Table. Age Structure of Patients by Years of Observation
| Years | Up to 1 month (abs) | 1-3 months (abs) | 4-6 months (abs) | 7-11 months (abs) | 1-3 years old (abs) | 4-6 years old (abs) | 7-10 years old (abs) | 11-17 years old (abs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 36 | 40 | 14 | 11 |
| 2022 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 24 | 31 | 20 | 24 |
| 2023 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 27 | 24 | 48 |
Boys were affected more often than girls (54.4% and 45.6% respectively; p < 0.05); urban residents predominated – 287 (90.8%). Those attending childcare institutions numbered 286 (90.5%).
The disease was registered throughout the year (see Fig. 1) with some predominance in the spring-summer period – 184 (58.2%) and the highest number of patients in this season in 2022.
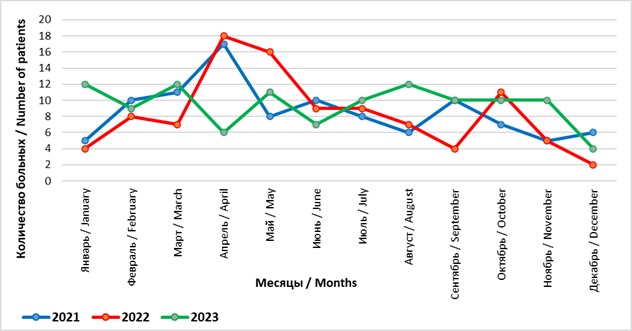
Fig. 1. Distribution of Patients by Year and Month of Observation
Concomitant pathology was detected in 82 (25.9%) patients: atopic dermatitis in 41 (13.0%); chronic adenoiditis and tonsillitis in 25 (7.9%); neurological disorders (epilepsy, cerebral palsy, intellectual disability, autonomic nervous system dysfunction) in 8 (2.5%); anemia in 4 (1.3%); enterobiasis in 2 (0.6%); diabetes mellitus in 1 (0.3%); and congenital heart disease in 1 (0.3%).
The disease was of moderate severity in the majority of patients (312 – 98.7%), and severe in 4 (1.3%). The severity of the condition was due to encephalitic reactions (febrile seizures, somnolence, nocturnal panic attacks) against the background of intoxication syndrome in children with concomitant neurological pathology.
Complications were identified in 43 (13.6%) patients: otitis – 23 (53.5%), sinusitis – 10 (23.3%), paratonsillitis – 1 (2.3%), stomatitis – 3 (6.9%), reactive pancreatopathy – 6 (14.0%).
Patients were admitted to the hospital on day 8.0 ± 0.30 of illness with complaints of fever, sore throat, nasal congestion, general weakness, lethargy, and enlarged cervical lymph nodes. Acute onset of IM was noted in 249 (78.8%) children. Fever was observed in all patients: up to 38.0°C – 19 (6.0%), from 38.0 to 39.5°C – 242 (76.6%), and above 39.5°C – 55 (17.4%). The duration of the febrile period was 9.43 ± 0.08 days.
Impaired nasal breathing was detected in 252 (79.7%) patients, and in 91 (36.1%) children it was severe and accompanied by snoring at night. Puffiness of the eyelids and facial swelling were observed in 65 (20.6%) individuals.
Skin rash was noted in 63 (19.9%) children, appearing on day 8.63 ± 0.08 of illness, accompanied by itching in 5 (7.9%) individuals. In 50 (79.4%) patients the rash was maculopapular, in 6 (9.5%) – finely spotted, in 5 (7.9%) – papular, and in 2 (3.2%) – petechial. In 47 (74.6%) children, the exanthema was bright red; in the rest, pale pink. Multiple rash elements were found in 55 (87.3%) individuals. In 44 (69.8%) patients, the eruptions spread over the entire body; in the rest, the elements were isolated on the face, trunk, or limbs. In 43 (68.3%) children, the exanthema was associated with the pre-hospital use of semi-synthetic penicillins (amoxicillin, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid).
Icterus of the skin and sclera was diagnosed in 8 (2.5%) patients.
Sore throat was noted in 191 (60.4%) children: moderate intensity – 140 (73.3%), severe – 39 (20.4%). Plaques on the tonsils were detected in 260 (82.3%) individuals: in lacunae – 231 (88.8%), in the form of follicles – 29 (11.2%). Yellow purulent plaques were observed in 111 (42.7%), white plaques in 149 (57.3%) patients.
Lymph node enlargement was registered in the majority (291 – 92.1%) of patients, with a diameter of 2.23 ± 0.06 cm, predominantly in the cervical group (258 – 88.7%) either isolated or in combination with others. In 86 (29.6%) individuals, the lymph nodes were painful and sensitive to palpation.
Abdominal pain was noted only in 21 (6.6%) patients, of moderate intensity, localized: in the right hypochondrium – 11 (52.4%), in the left hypochondrium – 4 (19.0%), in the epigastrium and periumbilical area – 6 (28.6%) children. Liver enlargement up to 1.98 ± 0.05 cm below the costal margin was diagnosed in 263 (83.2%) patients; spleen enlargement up to 1.43 ± 0.07 cm – in 139 (44.0%).
In the complete blood count, the leukocyte count was 14.54 ± 0.30 (×10⁹/L), band neutrophils – 3.48 ± 0.12 (%), segmented neutrophils – 34.06 ± 0.23 (%), eosinophils – 2.65 ± 0.89 (%), lymphocytes – 46.49 ± 0.35 (%), broad-plasma lymphocytes – 11.66 ± 0.50 (%), monocytes – 7.24 ± 0.66 (%), platelets – 206.11 ± 0.46 (%), ESR 21.91 ± 0.56 (mm/h). Leukocytosis was observed in 277 (87.7%) patients: mild (9.0–15.0×10⁹/L) – 153 (55.2%), moderate (15.1–20.0×10⁹/L) – 86 (31.1%), high (more than 20.1×10⁹/L) – 38 (13.7%). ESR above 20 mm/h was registered in 168 (53.2%) patients. Atypical mononuclear cells were detected in 165 (52.2%) children on day 6.63 ± 0.33 of illness and persisted for an average of 10.80 ± 0.65 days. The mean number of atypical mononuclear cells was 19.77 ± 0.79%; more than 30% – in 32 (19.4%) patients.
In the biochemical blood analysis, the level of total bilirubin was 6.86 ± 0.41 µmol/L, ALT – 91.66 ± 0.47 U/L, AST – 83.51 ± 0.68 U/L, alkaline phosphatase – 232.17 ± 0.44 U/L, CRP – 23.24 ± 0.06 mg/L, total protein – 70.25 ± 0.34 g/L, creatinine – 46.80 ± 0.07 µmol/L, urea – 3.66 ± 0.05 mmol/L, glucose – 4.87 ± 0.05 mmol/L. In 8 patients with icteric forms of IM, an increase in total bilirubin from 27.1 to 67.9 µmol/L was observed, due to the direct fraction. Elevated transaminase levels (ALT, AST) were registered in 173 (54.7%) individuals: up to 200 U/L – 136 (78.6%), from 200 to 400 U/L – 31 (17.9%), and above 400 U/L – 7 (4.0%).
An increase in CRP was noted in 118 (37.3%) children. Among patients with tonsillar plaques (260 individuals), CRP was elevated only in 101 (38.8%), which likely indicates a viral etiology of tonsillitis in the remaining patients.
The mean urine amylase level was 417.25 ± 0.08 U/L. In 6 (1.9%) children with reactive pancreatopathy, an increase in urine alpha-amylase above 500 U/L was observed: up to 700 U/L – in 3, from 700 to 1000 U/L – in 2, and above 2000 U/L – in 1 child.
According to abdominal ultrasound, 54 (17.1%) patients had liver enlargement, 224 (70.9%) – spleen enlargement, 105 (33.2%) – signs of mesadenitis, 5 (1.6%) – enlargement and diffuse changes in the pancreas.
The diagnosis was verified by ELISA in 293 (92.7%) patients on day 9.89 ± 0.31 of illness, and by PCR in 48 (15.2%). Primary herpesvirus infection was detected in 229 (72.5%) individuals: EBV – 132 (57.6%), CMV – 8 (3.5%), HHV-6 – 4 (1.7%); EBV and CMV – 85 (37.1%). Among these, Epstein-Barr virus dominated – in 217 (94.8%) either isolated (60.8%) or in combination with cytomegalovirus (39.2%). Herpesvirus reactivation was noted in 87 (27.5%) patients: CMV against the background of primary EBV infection in 84 (96.6%) children; EBV reactivation – in 2 (2.3%), EBV and CMV – in 1 (1.1%).
In 12 (3.8%) patients, the disease was combined with acute respiratory viral infections: adenoviral – 6 (50.0%), rhinoviral – 5 (41.7%), parainfluenza – 1 (8.3%). One child (0.3%) with IM was diagnosed with norovirus infection.
In 19 (7.3%) patients with tonsillar plaques, the following were isolated by bacteriological method: Staphylococcus aureus – 12 (63.2%), Streptococcus pyogenes – 2 (10.5%), Pseudomonas aeruginosa – 1 (5.3%), fungi of the genus Candida – 4 (21.0%) individuals.
In treatment, only 9 (2.8%) patients received acyclovir as etiotropic therapy. Children with tonsillitis – 260 (82.3%) and bacterial complications – 33 (10.4%) were prescribed antibiotics (ceftriaxone, cefixime). Infusion therapy was administered to 8 (2.5%) patients. Patients with severe allergic reactions and airway obstruction – 62 (19.6%) received systemic or inhaled glucocorticosteroids.
The mean hospital stay was 6.38 ± 0.12 days.
Clinical Case. We present a clinical case of the icteric form of infectious mononucleosis in a 13-year-old girl. She fell acutely ill on 17.10.23 with fever up to 38.5-39°C and nasal congestion; she took only antipyretics. On 21.10, she was examined by a local pediatrician and prescribed amoxicillin. On the 6th day of illness, she developed sore throat, dark urine, icteric sclera and skin (Fig. 2), and a single episode of vomiting. Febrile fever and nasal congestion persisted throughout. On 23.10, she was hospitalized. Her condition upon admission was of moderate severity, lethargic, with decreased appetite; temperature 37.8°C, RR 20/min, HR 120/min, BP 100/60 mm Hg. Icteric sclera and skin were noted, impaired nasal breathing without discharge, bright hyperemia in the pharynx, tonsils grade 2 with plaques in the lacunae bilaterally (Fig. 3); enlargement of the entire cervical lymph node group up to 1.0 cm, submandibular nodes up to 2.0 cm with moderate pain on palpation, liver – up to 2.0 cm, spleen – up to 1.0 cm below the costal margin. On 24.10, temperature of 39°C and sore throat persisted, accompanied by epigastric pain, nausea, and a single episode of vomiting. On 28.10 (day 12 of illness), a bright maculopapular rash appeared on the face, trunk, and limbs, increasing and tending to coalesce in the following days (Fig. 4, 5). The complete blood count showed leukocytosis 16.2×10⁹/L, lymphocytosis 86.2%, atypical mononuclear cells up to 31%, ESR up to 44 mm/h. Biochemical blood analysis showed increased bilirubin up to 126.1 µmol/L due to the direct fraction (120 µmol/L) and transaminases (ALT 307.6 U/L, AST 202.1 U/L); normal CRP (0.6 mg/L). ELISA of serum for markers of viral hepatitis was negative; antibodies to EBV VCA IgM with CP=10.0 and to EA IgG with CP=9.0 were detected; antibodies to CMV IgG with CP=15.0. PCR of blood plasma for EBV DNA was positive, CMV DNA – not detected. Throat swab for flora showed no microbial growth. Abdominal ultrasound revealed splenomegaly and mesenteric lymph nodes up to 15 mm, and thickened walls of the gallbladder. Diagnosis: Infectious mononucleosis caused by EBV (ELISA blood EBV VCA IgM CP=10.0; EA IgG CP=9.0, PCR EBV DNA "+" from 24.10.23), typical, icteric form, moderate severity. Complication: Amoxicillin exanthema. Treatment included diet, ceftriaxone 1.0 g twice daily IM for 7 days, fluconazole for 7 days, infusion therapy (0.9% sodium chloride, 5% glucose), prednisolone 60 mg IM #2, ursodeoxycholic acid, symptomatic therapy. Temperature normalized on day 15 from onset, fading of the rash, disappearance of skin icterus and tonsillar plaques – on day 21.
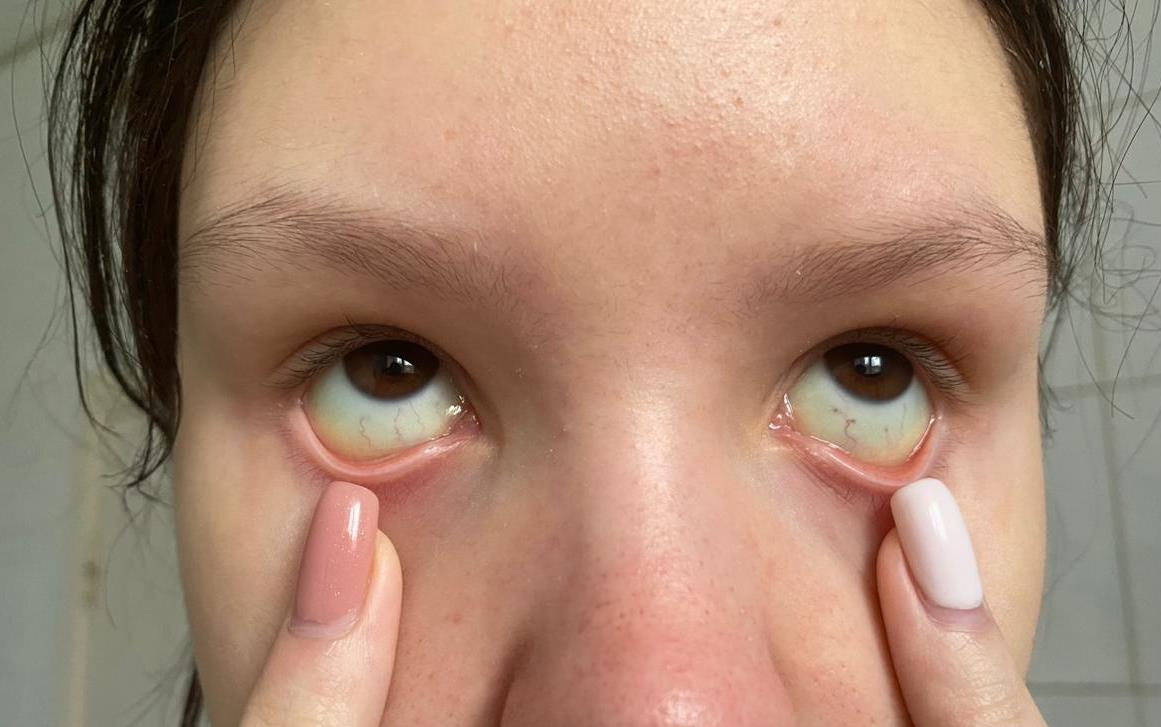
Fig. 2. Icteric Sclera
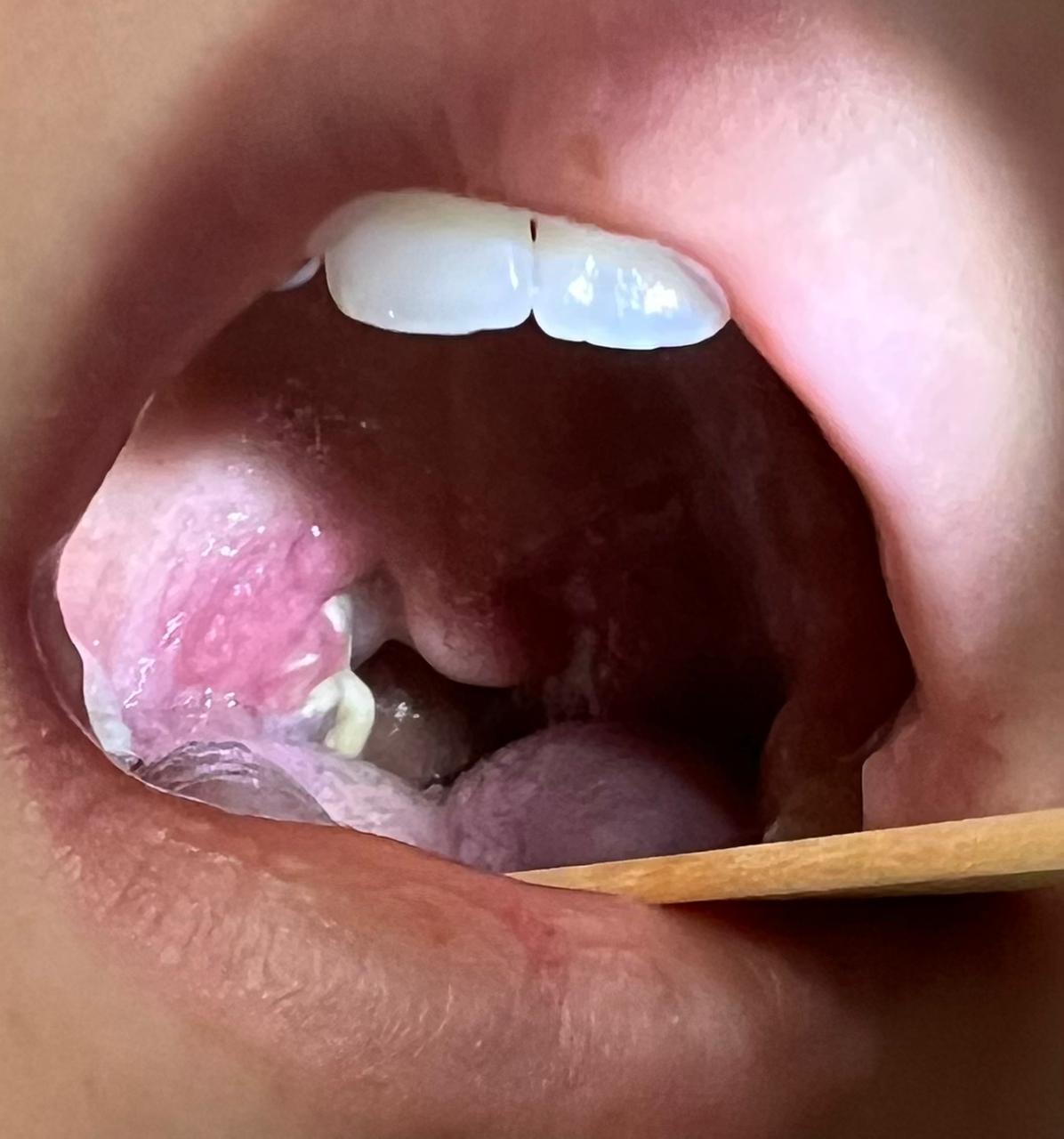
Fig. 3. Plaques on the Tonsils
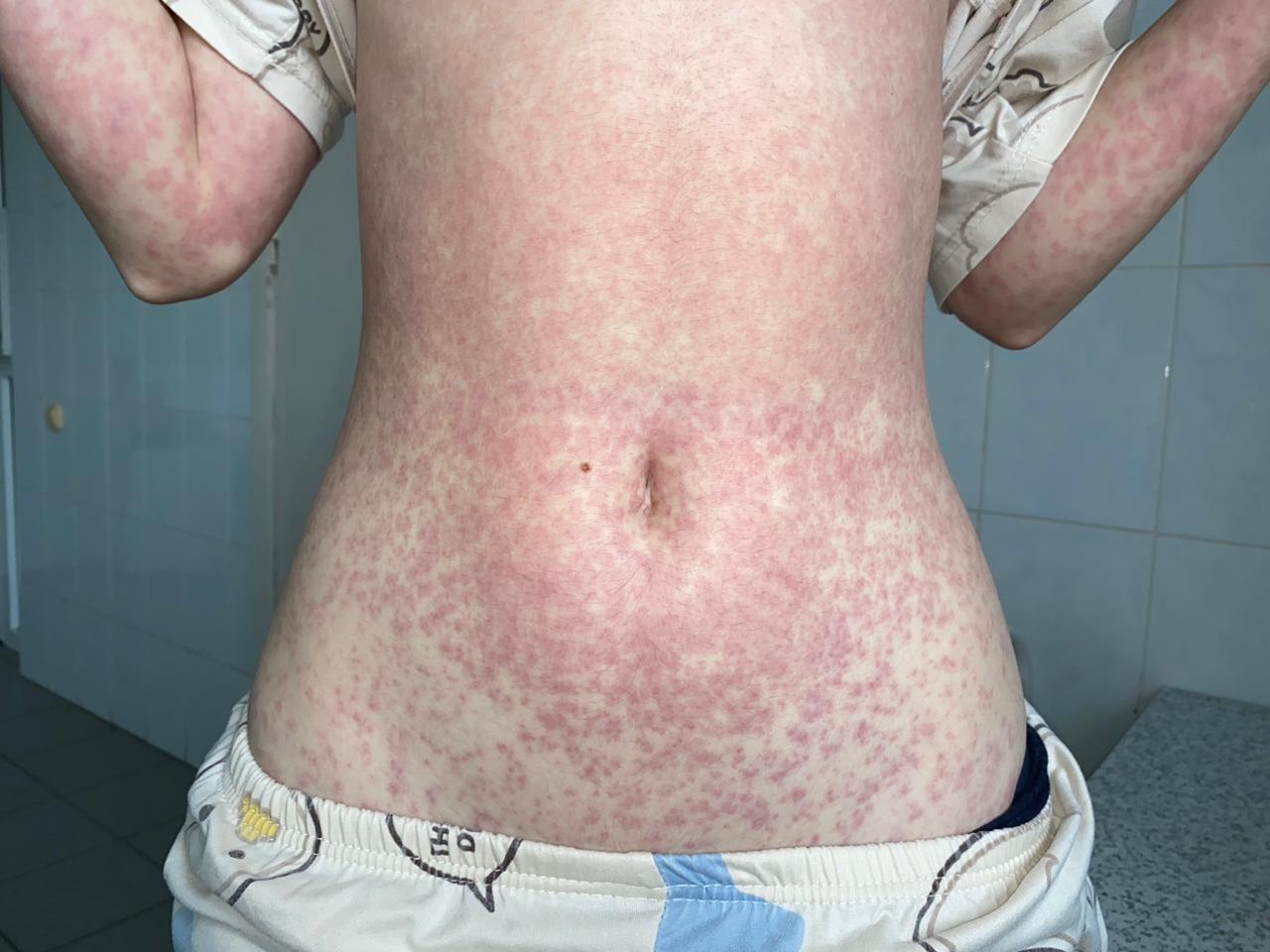
Fig. 4. Amoxicillin Rash on the Trunk
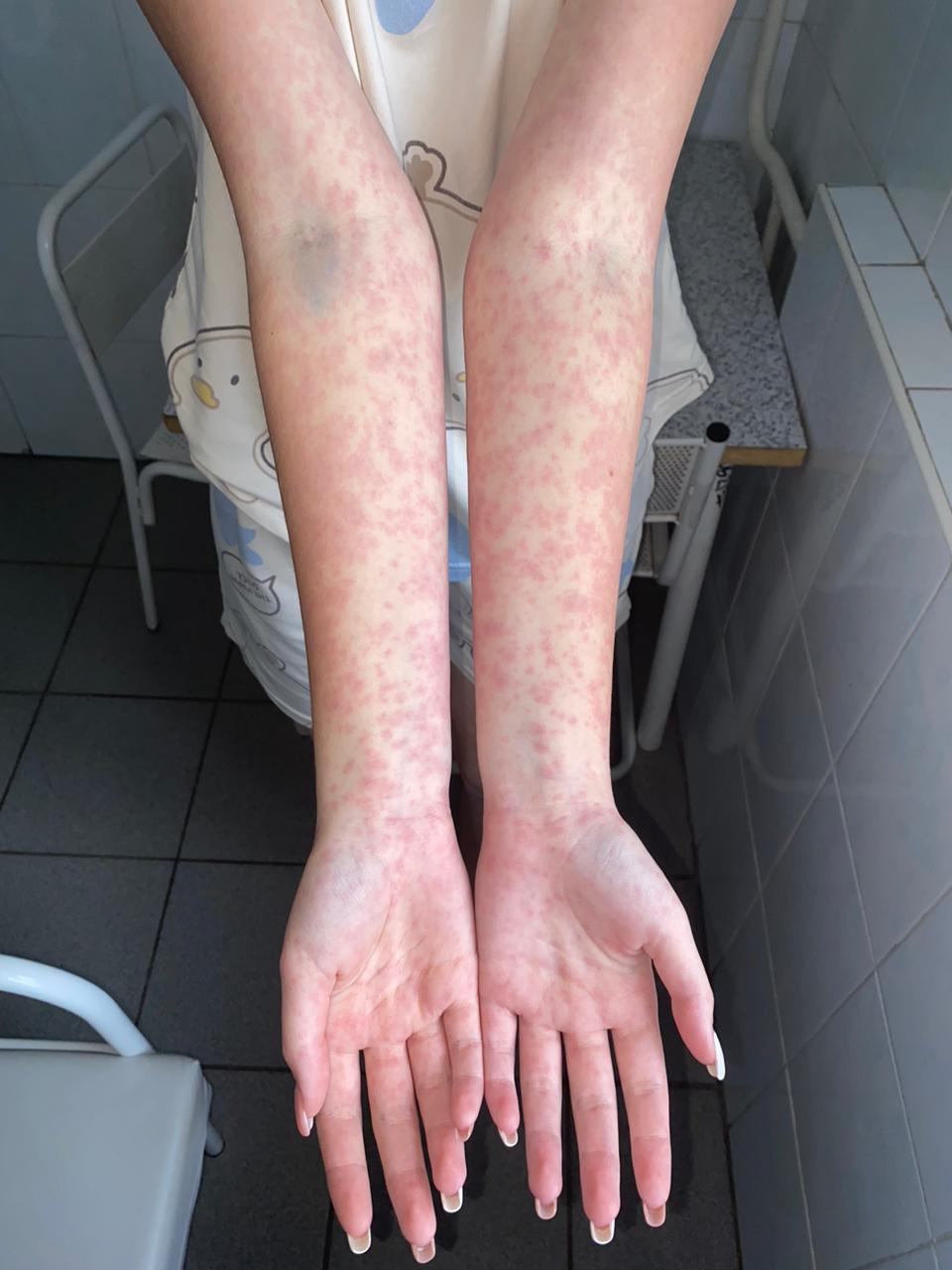
Fig. 5. Amoxicillin Rash on the Extremities
In this case, a 13-year-old child had infectious mononucleosis in an icteric form with an increase in bilirubin level to 126 µmol/L, transaminases – to 300 U/L, with characteristic clinical (prolonged febrile fever, impaired nasal breathing, tonsillitis, polyadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly) and laboratory manifestations (lymphocytic leukocytosis with atypical mononuclear cells). The prescription of amoxicillin at the pre-hospital stage led to the appearance of exanthema on the 12th day from the onset of the disease.
Conclusions
Children aged 4 to 6 years (31.0%) and 11 to 17 years (26.3%) were most frequently affected by infectious mononucleosis; the lowest incidence among children under one year (1.0%) is likely due to limited contacts and specific maternal antibodies received transplacentally.
The disease was registered throughout the year with some predominance in the spring-summer period (58.2%).
The majority (98.7%) of children had IM of moderate severity. Icteric forms were detected in 2.5%, complications (otitis, sinusitis, paratonsillitis, stomatitis, reactive pancreatopathy) – in 13.6% of patients.
Acute onset of the disease was registered in 78.8% of children. Fever was observed in all patients, lasting 9.43 ± 0.08 days. The majority of patients had lymphadenopathy (92.1%), tonsillar plaques (82.3%), impaired nasal breathing (79.7%), and hepatomegaly (83.2%). Skin rash appeared on day 8.63 ± 0.08 of illness in 19.9% of patients, and in 68.3% of these children it was associated with the use of semi-synthetic penicillins.
In the complete blood count, leukocytosis was observed in the majority of patients (87.7%); ESR greater than 20 mm/h – in 53.2% of individuals. Atypical mononuclear cells were detected on day 6.63 ± 0.33 of illness only in 52.2% of children and persisted for 10.80 ± 0.65 days. The mean number of atypical mononuclear cells was 19.77 ± 0.79 (%).
In the biochemical blood analysis, elevated transaminase levels were registered in 54.7% of children, predominantly up to 200 U/L (78.6%). In patients with icteric forms of IM, the total bilirubin level was not very high. Among children with tonsillar plaques, CRP was above normal only in 38.8%, which likely indicates a viral etiology of tonsillitis in the remaining patients.
Primary infection with EBV, CMV, and HHV-6 was detected in 72.5% of patients, among whom Epstein-Barr virus dominated (94.8%) either isolated (60.8%) or in combination with cytomegalovirus (39.2%). Herpesvirus reactivation was noted in 27.5% of patients, most often CMV against the background of primary EBV infection (96.6%).
Conclusion
The conducted analysis showed that the clinical picture of infectious mononucleosis still retains characteristic symptoms: fever, impaired nasal breathing, tonsillitis, lymphadenopathy, exanthema, hepatomegaly and splenomegaly. Icteric forms of the disease are rare. In most patients, the appearance of a rash is associated with the prescription of semi-synthetic penicillins at the pre-hospital stage. The appearance of atypical mononuclear cells in only half of the patients complicates diagnosis based on the complete blood count. Epstein-Barr virus remains dominant in primary infection, either alone or in combination with cytomegalovirus. Reactivation in almost all patients is due to CMV against the background of primary EBV infection. In most children with tonsillar plaques, a low CRP level indicates a viral etiology of tonsillitis and does not require the prescription of antibacterial therapy.
References
1. Solomay T.V., Semenenko T.A. Epstein-Barr viral infection is a global epidemiological problem. Problems of Virology (Voprosy Virusologii). 2022; 67(4): 265-277. (In Russ.) DOI: 10.36233/0507-4088-122.
2. Demina O.I., Chebotareva T.A., Mazankova L.N., Tetova V.B., Uchaeva O.N. Clinical manifestations of infectious mononucleosis in primary or reactivated herpes virus infection. Ros Vestn Perinatol i Pediatr. 2020; 65:(1): 37-44. (In Russ.) DOI: 10.21508/1027-4065-2020-65-1-37-44.
3. Drozdova N.F., Fazylov V.H. Infectious mononucleosis caused by Epstein – Barr virus: clinical and pathogenic aspects (review). The Vestnik sovremennoj klinicheskoj meditsiny. 2018;11(3):59-61. (In Russ.)
4. Savitskaya V.V., Tarasova E.E. Importance of the ELISA method in the diagnosis of EBV. Sakharov Readings of 2018: Environmental Problems of the 21<sup>st</sup> Century. Proceedings of the 18<sup>th</sup> International Scientific Conference. S.A. Maskevich, S.S. Poznyak (eds). Minsk: IVTS Minfina. 2018; 1: 327-328 (In Russ.)
5. Eshmolov S.N., Klimovitskaya E.G., Kuzmina M.N., Sitnikov I.G. Lesions of the nervous system in herpesvirus infections. Children's infections. 2022;4(81):15-20. (In Russ.) DOI: 10.22627/2072-8107-2022-21-4-15-20.
6. Balmasova I.P., Sepiashvili R.I. Cytomegalovirus and natural killers: new approaches to the problem. Аllergologiya i immunologiya. 2016;17(1):12-17. (In Russ.)
7. Kotlova V.B., Kokoreva S.P., Trushkina A.V. Оptimization of Treatment EBV Infectious Mononucleosis in Children. Detskie infektsii. 2015;14(3):43-48. (In Russ.) DOI: 10.22627/2072-8107-2015-14-3-43-48.
8. Permyakova A.V., Pospelova N.S., Deryusheva A.Yu. Results of prospective follow-up observation of acute cytomegalovirus infection in children. Permskii meditsinskii zhurnal. 2019;36(1):91-96 (In Russ.)
9. Martynova G.P., Bogvilene Ja.A., Iskra I.P., Stroganova M.A., Gura O.A., Sokolova O.A. The clinical laboratory characteristic of infectious mononucleosis in children. Lechenie i profilaktika. 2015;4:29–35 (In Russ.)
10. Postanogova N.O., Sofronova L.V. Blood counts in children with infectious mononucleosis depending on the ethology of the disease in the acute period and follow-up. Voprosy prakticheskoj pediatrii. 2016;11(3):22-25. (In Russ.) DOI: 10.20953/1817-7646-2016-3-22-25.
11. Simovanyan E.N., Denisenko V.B., Grigoryan A.V., et al. Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Children: Improving the Diagnosis and Treatment Program. Detskie infektsii. 2016;15(1):15-24. (In Russ.) DOI: 10.22627/2072-8107-2016-15-1-15-24.
About the Authors
M. N. KuzminaРоссия
Maria N. Kuzmina, Cand. Sci. (Med.), Assistant Professor
Department of Infectious Diseases, Epidemiology and Pediatric Infections
Yaroslavl
Competing Interests:
Authors declare no conflict of interest requiring disclosure in this article
S. N. Eshmolov
Россия
Sergey N. Eshmolov, Cand. Sci. (Med.), Associate Professor
Department of Infectious Diseases, Epidemiology and Pediatric Infections
Yaroslavl
Competing Interests:
Authors declare no conflict of interest requiring disclosure in this article
E. G. Klimovitskaya
Россия
Elizaveta G. Klimovitskaya, Cand. Sci. (Med.), Associate Professor
Department of Infectious Diseases, Epidemiology and Pediatric Infections
Yaroslavl
Competing Interests:
Authors declare no conflict of interest requiring disclosure in this article
I. G. Sitnikov
Россия
Ivan G. Sitnikov, Dr. Sci. (Med.), Professor, Head of the Department
Department of Infectious Diseases, Epidemiology and Children's Infections
Yaroslavl
Competing Interests:
Authors declare no conflict of interest requiring disclosure in this article
Review
For citations:
Kuzmina M.N., Eshmolov S.N., Klimovitskaya E.G., Sitnikov I.G. Modern infectious mononucleosis in children: results of own observations. Patient-Oriented Medicine and Pharmacy. 2025;3(3):77-85. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.37489/2949-1924-0106. EDN: YTCKUN
JATS XML


































.png)
